Diamond: Properties, Benefits & Meanings

Diamond Overview
Diamonds are among the most valuable and sought-after gems in the world. These gems are considered the purest and most beautiful form of crystallized carbon. They are commonly used in jewelry and for industrial purposes. A diamond’s beauty comes from its unique geometric structure. They are valued for their hardness, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. In addition, they have a rich history, special properties, and deep spiritual significance.
Their beauty and rarity have made them one of the most popular gems in the world. Their sparkling appearance and durability have made them the ultimate symbol of love, commitment, and wealth. But what makes them so special, and what do they represent? This blog post will explore diamonds’ physical and spiritual properties and how they’ve captured our imaginations for centuries.
What Is Diamond?
Diamond is a naturally occurring mineral that is composed of pure carbon. It is the hardest substance known to man and is one of the world’s most valuable and sought-after gems. The crystal structure is unique, giving it its exceptional hardness, high thermal conductivity, and high refractive index, making it one of the most brilliant gems.
They are formed deep within the earth’s mantle under extreme pressure and temperature. They can also be found in alluvial deposits, where they have been eroded from their source and deposited in riverbeds and on the ocean floor.
They are available in many colors, including colorless, yellow, pink, blue, green, and black. In addition, they can be cut and polished into various shapes and sizes, making them versatile and adaptable for use in jewelry.
How is Diamond Formed?
Diamonds are formed deep within the earth’s mantle, over 100 miles below the surface, under extreme pressure and temperature conditions. They are believed to be formed from carbon-rich material brought to the surface through volcanic eruptions. This carbon-rich material cools and solidifies into a crystal structure.
There are two types of formation: primary and secondary. Primary diamonds are formed deep within the earth’s mantle. Secondary diamonds are formed near the surface. They are found in alluvial deposits, where they have been eroded from their source and deposited in riverbeds and on the ocean floor.
The process of formation needs to be better understood. Still, it is thought to occur over millions of years and requires a combination of intense pressure and high temperatures. As a result, they can be found in various rock formations, including kimberlite pipes and lamproite rocks.
Physical Properties of Diamond
| Mineral Class | Diamond |
| Formula | C |
| Crystal System | Isometric |
| Color | Many |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 10 |
| Refractive Index | 2.417 – 2.419 |
| Fracture | Irregular/Uneven |
| Luster | Adamantine |
| Specific Gravity | 3.1 – 3.5 |
| Transparency | Transparent to Opaque |
Etymology of Diamond
The word “diamond” comes from the Greek word “adamas,” which means “unbreakable” or “invincible.” This name reflects the exceptional hardness and durability of diamonds, which have long been considered one of the world’s most valuable and prized gems.
Their use in jewelry can be traced back to ancient India, where they were used in religious ceremonies and as talismans to ward off evil. The ancient Greeks and Romans also valued these gems for their beauty and rarity. As a result, they were often set into gold and used to decorate the armor and weapons of warriors.
Over time, they became associated with wealth, power, and luxury. In addition, they became a symbol of love and commitment when used in engagement rings. As a result, these gems continue to be one of the most sought-after gems in the world, and their popularity shows no signs of fading.
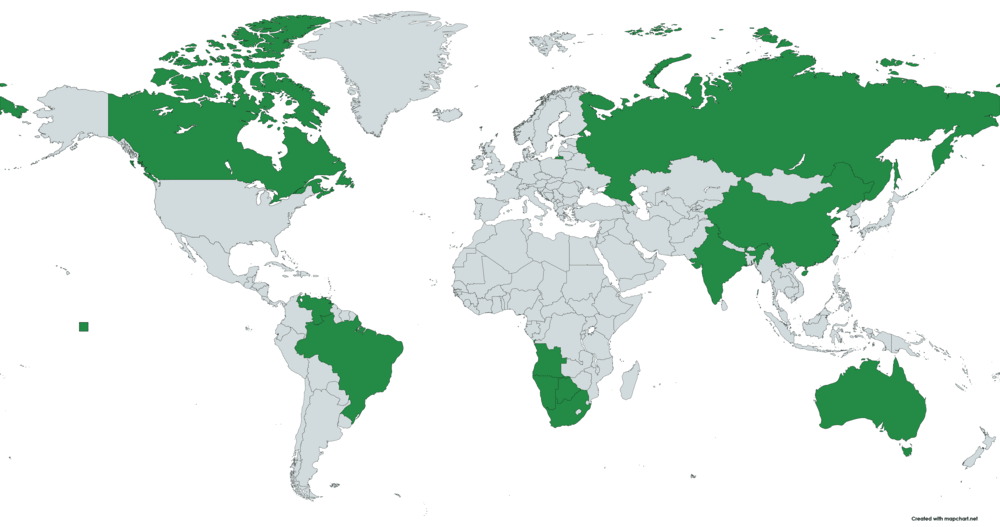
Where is Diamond Found?
Diamonds are found in many countries worldwide. The list includes only some of the largest producers.
- Russia
- Australia
- Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
- Canada
- Angola
- Botswana
- South Africa
- Namibia
- Zimbabwe
- Lesotho
- China
- India
- Brazil
- Sierra Leone
- Liberia
- Guinea
- Ghana
- Ivory Coast
- Central African Republic
- Venezuela

Diamond Appearance
Diamonds are formed when carbon atoms bond with other elements inside the earth’s crust. This process creates a unique crystalline structure that gives them high dispersion, a distinct appearance, and a brilliant shine.
The appearance can range from pure and flawless to chipped and splintered. They can also be found in various shapes and sizes, from round to heart-shaped to square. The color, shape, and quality can vary significantly depending on the type of stone, the conditions under which it was mined, and other factors.
Diamonds come in many colors, including yellow, blue, pink, and dark red. Their different hues can be attributed to the various elements present in the earth’s crust from which they are formed. The unique combination of cut, color, clarity, and carat weight contributes to its overall appearance, and these factors are considered when determining the value of a piece.
Types of Diamond
There are several different types of diamonds, each with unique properties and characteristics. Some of the most common types include:
- Natural diamonds are formed deep within the earth and have not been artificially altered or treated in any way.
- Synthetic diamonds are created in a laboratory setting using high pressure and high temperature (HPHT) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) methods. Synthetic pieces have the same physical and chemical properties as natural ones but are much less expensive.
- Treated diamonds are natural but have been altered or treated in some way to improve their appearance or quality. Treatment methods include irradiation, which changes the color, and fracture filling, which hides cracks or inclusions.
- Type I: These are the ones that contain a relatively small amount of nitrogen impurities, which give them a yellow or brown color.
- Type II: This type contains little or no nitrogen impurities and is usually colorless or near-colorless.
- Fancy colors have a unique and intense colors, such as blue, green, yellow, pink, or red. Fancy color gems are extremely rare and highly valuable.
- Industrial grade is for industrial use only. These are not of gem quality. These are usually brown, yellow, gray, green, or black and lack the clarity and brilliance of a gemstone.
Different types of diamonds have varying physical and chemical properties. As a result, they can be used in various jewelry applications, from engagement rings to bracelets and necklaces.
Grading System Of Diamonds
The grading system refers to evaluating the quality based on several factors known as the “Four Cs”: Carat Weight, Cut, Clarity, and Color. Professional gemologists use this system to determine the value and quality to help consumers make informed decisions when purchasing jewelry. GIA [Gemological Institute of America], an institute dedicated to education and research in gemology] is responsible for developing the four C’s of evaluating Diamond quality and also provides identification and grading for gemstones. Here is How GIA grades diamonds.
- Carat weight: This refers to the size and is measured in carats. One carat is equal to 200 milligrams, or 0.2 grams.
- Cut: The cut refers to the angles and proportions and is a major factor in determining sparkle and brilliance. A well-cut piece will have the optimal combination of depth, table size, and angles to maximize the reflection and refraction of light.
- Clarity: Clarity refers to the presence or absence of internal or external inclusions or blemishes. The clarity is rated on a scale that ranges from “included” (I1) to “flawless” (FL).
- Color: The color is rated on a scale that ranges from “D” (no hue) to “Z” (light yellow or brown hue). A piece that is rated “D” is considered to be completely colorless. In contrast, a sample rated “Z” has a noticeable yellow or brown tint.
The combination of these Four Cs determines overall quality and value. The grading system is an international standard. Professional gemologists use a standardized set of criteria to evaluate the overall rating. This helps to ensure that diamonds are consistently and accurately assessed and that consumers clearly understand the quality when purchasing.

Diamond Value and Price
Various factors determine the value and price of a diamond, and the 4 Cs are the most important factors to consider when evaluating its worth.
- Carat weight: The carat weight refers to its size and is the unit of measurement used to weigh. The larger the piece, the higher its carat weight and value.
- Cut: A cut refers to how it has been cut and polished to enhance its brilliance, fire, and overall beauty. A well-cut piece will have a higher value than a poorly-cut piece.
- Clarity: Clarity is graded on a scale that ranges from included to flawless. Flawless pieces are extremely rare and highly valuable.
- Color: While a pure piece is thought to be colorless, it can come in various colors, including yellow, pink, blue, green, and black. Colorless pieces are highly prized, and their value increases as the color become more intense.
In addition to the 4 Cs, other factors that can affect the value and price include the rarity, demand, origin, and reputation of the seller. It’s also important to consider the overall quality, as well as its cut, symmetry, and polish.
When buying, it’s important to research. First, choose a reputable jeweler who can provide you with a certificate of authenticity and a detailed description of the quality and value.
How Can You Tell if Diamond Is Real?
Determining the authenticity of a diamond can be challenging, as synthetic and simulants have become increasingly sophisticated and difficult to distinguish from real ones. However, there are several tests that you can use to determine if a sample is real or not.
- Visual Inspection: A trained gemologist can determine if a piece is real or not based on its physical appearance, including its cut, clarity, color, and overall quality.
- The Fog Test involves breathing on the sample and observing how it reacts to the fog. If the fog quickly dissipates, it is likely real. It may be a simulant if the fog lingers for a few seconds.
- The UV Light Test: A real piece will emit a blue glow when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, while most simulants will not.
- The Thermal Conductivity Test: These gems are excellent heat conductors, which will transfer heat quickly from one point to another. A real sample will quickly dissipate heat when you touch it, while simulants will not.
- The Loupe Test: A jeweler’s loupe is a small magnifying glass that can inspect a piece for inclusions, blemishes, and other characteristics of a real sample.
International standards like the 4Cs have been established by organizations such as the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and the American Gem Society to determine the authenticity and quality of diamonds. These organizations use rigorous testing methods, including X-ray spectroscopy and microscopic examination, to determine its characteristics and properties and issue certificates of authenticity.
While several tests can determine if a sample is real, it’s always best to work with a knowledgeable and experienced gemologist who can help you authenticate the piece and provide you with a certificate of authenticity.

What Does Diamond Symbolize?
Diamonds have long been considered one of the most precious gems in the world, and they have a rich symbolic history that spans cultures, religions, and civilizations. Some of the most common symbolic meanings associated with it include:
- Love and commitment: These gems have long been associated with passion and dedication. They are often given as engagement and wedding rings to symbolize the couple’s love and devotion to one another.
- Strength and durability: The gems are known for their incredible strength and durability, and they are often symbolized as representing inner strength, resilience, and a commitment to endure.
- Wealth and success: These gems are expensive and highly prized, and they have long been associated with wealth, luxury, and success. They are often seen as symbols of financial stability and prosperity.
- Purity and clarity: These precious stones are known for their sparkling beauty and clarity and are often associated with purity and innocence. They are often given as gifts to symbolize the giver’s love and affection for the recipient.
- Spiritual enlightenment: Some spiritual traditions are symbols of spiritual growth and inner peace, as they are believed to hold the energy of the universe within them.
Diamonds have a rich and complex symbolic history, and their meaning can vary greatly depending on the individual and the cultural context. Regardless of their symbolic meaning, they are widely recognized as one of the world’s most popular gemstones. They are highly prized for their timeless beauty and rarity.

Uses of Diamond
Diamonds are one of the most versatile and valuable materials on the planet. As a result, they have a wide range of uses in various industries. Some of the most common uses include:
- Jewelry: These gems are prized for their beauty and rarity, and they are widely used in jewelry making, including engagement and wedding rings, necklaces, earrings, and bracelets.
- Industrial applications: They are used in various industrial applications, including cutting, grinding, and polishing multiple materials, including glass, ceramics, and metals.
- Electronic Devices: They are used in various electronic devices, including computer hard drives and heat sinks, due to their ability to conduct heat and their electrical insulating properties.
- Abrasives: They are one of the hardest materials on the planet. The hardness makes them ideal for use in abrasive material for cutting, grinding and polishing various surfaces.
- Medical equipment: They are used in medical equipment, such as surgical scalpels, due to their sharpness and durability.
- Scientific research: They are used in a wide range of scientific research applications, including experiments in high-pressure and high-temperature physics, as well as in the development of new technologies, such as quantum computing.
Is Diamond a birthstone?
Yes, a diamond is a birthstone. It is the traditional Birthstone for April. Birthstones are gemstones associated with each month of the year and are believed to bring good luck and provide protection to those born in that month.
It is a highly valued and prized gemstone widely recognized for its beauty and rarity. It has been a popular birthstone choice for centuries.

How To Take Care Of Diamond Jewelry?
Diamonds are valuable gemstones, and taking proper care of your jewelry can help maintain its beauty and luster for many years. Here are some tips for taking care of your jewelry:
- Clean regularly: Regular cleaning can help to remove dirt, oil, and other buildups that can dull the appearance of your gems. You can clean it with a soft cloth or a solution of warm water and mild soap.
- Store carefully: When not in use, store your jewelry in a soft cloth or a jewelry box to protect it from scratches and other damage. Avoid storing your jewelry near other gemstones or jewelry that can scratch or damage it.
- Handle with care: Avoid exposing your jewelry to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures. Always remove it before participating in physical activities that could cause damage.
- Avoid ultrasonic cleaners: While ultrasonic cleaners can be effective for cleaning other types of jewelry, they can damage the jewelry setting and cause the stones to come loose. If you need clarification on whether your jewelry is safe to clean with an ultrasonic cleaner, consult a professional jeweler.
- Have it professionally cleaned: Regular professional cleaning can help maintain your jewelry’s beauty and luster. An experienced jeweler can thoroughly clean your jewelry and inspect the setting to ensure it’s secure.
Following these tips can help ensure that your jewelry remains beautiful and valuable for many years.
FAQ
What are diamonds made of?
Diamonds are made of carbon, which is compressed and crystallized throughout millions of years. The pressure and heat of the earth’s mantle cause the carbon atoms to bond in a unique crystal structure that gives them hardness and brilliance.
How are diamonds mined?
Diamonds are typically mined from kimberlite pipes. The mining process involves extracting the kimberlite rock from the earth and processing it to separate the diamonds from other minerals.
How do you determine the value of a diamond?
The value of a diamond is determined by several factors, including its size, color, clarity, and cut. These factors are collectively known as the “4 Cs” of grading a gemstone. For example, a sample that is large, colorless, has high clarity, and is well-cut will be more valuable than one that is small, has a yellow tint, has inclusions, and is poorly cut.
Which Other Gemstones Pair Well With Diamonds in Jewelry?
Diamonds pair well with many other gemstones in jewelry, depending on the style and look you are trying to achieve. Some of the most popular gems to pair with it include:
Sapphire: A classic choice that adds blue color to diamond jewelry.
Emerald: A rich, green color that brings an organic feel to diamond jewelry.
Ruby: A vibrant red stone that adds a touch of glamor and luxury to diamond jewelry.
Amethyst: A deep purple color that complements diamonds and adds a touch of elegance to jewelry designs.
Pearls: A timeless classic that brings a soft, feminine touch to diamond jewelry.
Aquamarine: A pale blue gemstone that adds a touch of serenity and calm to diamond jewelry.
Morganite: A smooth, pink stone that brings a touch of romance and tenderness to diamond jewelry.
These are just a few of the many gemstones that pair well with diamonds in jewelry. When choosing a gem to pair with diamonds, consider the colors and styles you like and the overall look you are trying to achieve.