Colored Diamonds: Properties, Benefits & Meanings

Colored Diamonds Overview
Throughout history, diamonds have been associated with love, luxury, and exclusivity. Colored diamonds, also called fancy color diamonds or fancy diamonds, come in a stunning range of hues, from pale pink to deep blue, and are highly prized for their rarity, beauty, and symbolic meaning. These gems are incredibly rare, unique, and individual, as each colored diamond has its specific color and set of characteristics.
The intensity of the color is crucial when it comes to colored diamonds. A combination of hue, saturation, and tone determines the color. A diamond with a deep, vivid color will be more valuable than one with a pale or muted shade. Colored diamonds have been associated with various qualities and emotions throughout history.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the properties, benefits, and meanings of colored diamonds so that you can gain a better understanding of these fascinating gems.
What are Colored Diamonds?
Colored diamonds are a type of diamond that exhibits a noticeable color caused by certain trace elements in the diamond’s crystal lattice structure during its formation. These trace elements can include nitrogen, boron, or radiation. They can give diamonds a wide range of colors, including pink, blue, yellow, green, and even red.
Unlike traditional colorless diamonds, colored diamonds are graded based on their intensity of color, which is determined by a combination of hue, saturation, and tone. Colored diamonds are rare and highly prized for their unique beauty, individuality, and symbolic meaning.
How are Colored Diamonds Formed?
Colored diamonds are formed in the same way as traditional colorless diamonds, which is through intense pressure and heat deep within the Earth’s mantle. However, certain trace elements can become trapped within the diamond’s crystal lattice structure during the diamond’s formation process. These trace elements can include boron, nitrogen, hydrogen, or radiation, and they can affect the diamond’s color.
For example, the presence of boron can create a blue diamond, while nitrogen can create a yellow diamond. The amount and distribution of these trace elements within the diamond will determine the intensity and hue of the diamond’s color. Colored diamonds are much rarer than traditional colorless diamonds.
Physical Properties
| Mineral Group | Native Element |
| Formula | C (carbon) |
| Chemical Name: | Carbon |
| Color | Pink, blue, yellow, green, red, purple, brown, and black |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 10 |
| Refractive Index | 2.417 – 2.419 |
| Fracture | Conchoidal (smooth, curved surfaces) or splintery |
| Luster | Adamantine (brilliant shine) |
| Specific Gravity | 3.5 – 3.53 |
| Transparency | Translucent to Opaque |
Etymology
The word “diamond” comes from the Greek word “adamas,” which means unconquerable or invincible. It is fitting since diamond is Earth’s hardest naturally occurring substance. “adamas” was also used to refer to any hard sense, including steel and even the hardest rock.
“colored diamond” refers to any diamond with a noticeable hue, such as pink, blue, or yellow.
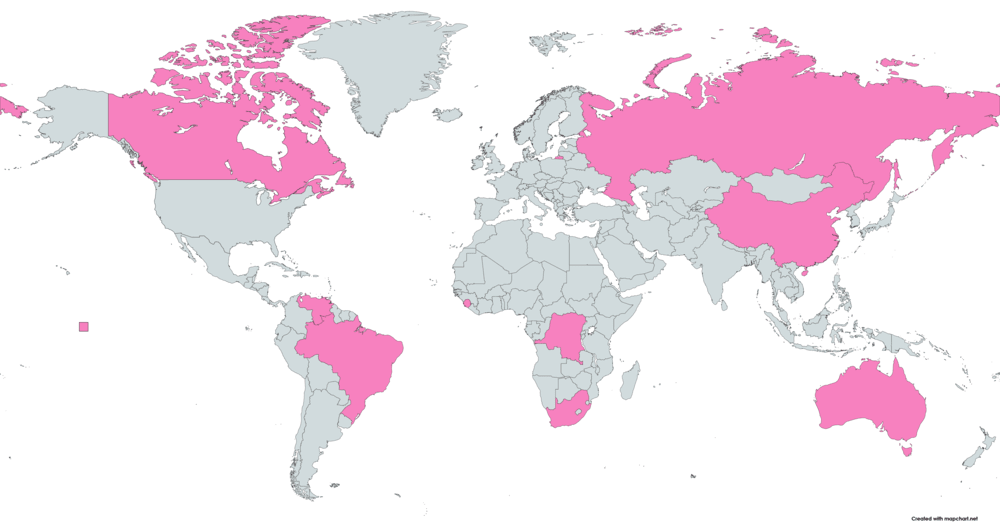
Where Are Colored Diamonds Found?
Here is a list of countries where colored diamonds are found:
- Australia
- South Africa
- India
- Canada
- Brazil
- Russia
- China
- Venezuela
- Democratic Republic of Congo
- Angola
- Sierra Leone

Colored Diamonds Appearance
Colored diamonds have a unique and striking appearance due to their noticeable hue, ranging from pale and subtle to intense. The specific appearance of a colored diamond depends on the hue, saturation, and tone of the diamond’s color.
Hue refers to the diamond’s dominant color, such as pink, blue, or yellow. Saturation refers to the intensity of the hue, ranging from pale to vivid. Tone refers to how light or dark the diamond appears.
For example, a pink diamond may have a pale pink hue, a medium saturation, and a light tone, resulting in a delicate and feminine appearance. On the other hand, a blue diamond may have a deep blue hue, a high saturation, and a dark tone, resulting in a dramatic and intense appearance.
The appearance of a colored diamond is also influenced by its cut and clarity. A well-cut diamond with good clarity can enhance the intensity of its color, making it even more striking and beautiful.
Natural Colored Diamonds Vs. Treated Colored Diamonds
Natural color diamonds: These are naturally formed with a distinct color due to the presence of specific chemical elements during their formation process. The color intensity can range from faint to vivid and is graded based on the intensity and hue of the color. Some popular natural color diamonds include pink, blue, yellow, and red.
Treated color diamonds: These have been treated or enhanced to change or improve their color. The most common treatment is irradiation, which involves exposing the diamond to radiation to alter its color. Another method is to apply a coating or layer on the surface of the diamond to change its color temporarily. Treated color diamonds are usually less valuable than natural color diamonds and are often disclosed as such when sold.
Do colored diamonds have 4CS?
Colored diamonds have 4Cs, just like white diamonds. However, the way the 4Cs are evaluated for colored diamonds is slightly different due to their unique characteristics. The 4Cs of diamonds are:
- Carat weight: This measures the weight of the diamond and is one of the most important factors that affect the value of a diamond.
- Color: This measures the color of the diamond, with colorless diamonds being the most valuable. For colored diamonds, the color intensity, hue, and saturation are evaluated.
- Clarity: This measures the presence of internal and external blemishes or inclusions in the diamond.
- Cut: This measures how the diamond is cut and polished, affecting its brilliance and fire.
The color grading system for colored diamonds differs from those used for white diamonds. Colored diamonds are graded on a scale that considers their color’s intensity, hue, and saturation, with the most valuable diamonds exhibiting a deep and vivid color saturation.
Types of Colored Diamonds
There are many colored diamonds, each with its unique color and characteristics. Here are some of the most well-known types of colored diamonds:
- Pink diamonds have a delicate and feminine pink hue and are among the rarest and most valuable colored diamonds.
- Blue diamonds: These diamonds have a deep and rich blue hue, which can range from pale blue to a deep blue similar to the color of the ocean.
- Yellow diamonds: These diamonds have a sunny and warm yellow hue ranging from pale yellow to vibrant canary yellow.
- Green diamonds: These diamonds have a rare and unique green hue ranging from a subtle mint green to a deep forest green.
- Red diamonds have a vivid and intense red hue and are among the rarest and most valuable colored diamonds.
- Brown diamonds: These diamonds have a warm and earthy brown hue ranging from light champagne to a deep chocolate brown.
- Black diamonds have a dramatic and mysterious black hue and are often used in edgy and modern jewelry designs.
- Gray diamonds: These diamonds have a cool and sophisticated gray hue ranging from light silver to dark charcoal gray.
- Purple diamonds have a romantic and regal purple hue, ranging from a subtle lavender to a deep grape purple.
Each type of colored diamond has its unique beauty and value, and the rarity and intensity of its color can greatly impact its worth.

Colored Diamonds Value and Price
The value and price of a colored diamond depend on several factors, including carat weight, cut, clarity, and color intensity.
The carat weight measures a diamond’s size, with larger diamonds being more valuable than smaller ones. However, the value of a colored diamond can increase exponentially with its carat weight, as larger and rarer colored diamonds are extremely rare and in high demand.
Cut is another important factor that affects a diamond’s value. A well-cut diamond with good proportions and symmetry will maximize its brilliance, fire, and color, making it more valuable.
Clarity is the absence of a diamond’s internal and external flaws or blemishes. The clarity of a colored diamond is less important than that of a colorless diamond, as color is the most significant factor determining the diamond’s value.
Color intensity is the most significant factor affecting the value and price of a colored diamond. The more intense and vivid the diamond’s color, the more valuable it is. The color of a colored diamond is graded on a scale from faint to fancy vivid, with fancy vivid diamonds being the rarest and most valuable.
Colored diamonds are extremely rare and valuable. Their price can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars per carat, depending on the abovementioned factors.
How Can You Tell if A Colored Diamond Is Real?
Several tests can be performed to determine if a colored diamond is real or not:
- Visual inspection: One of the easiest ways to identify a real colored diamond is by examining it closely under a magnifying glass or jeweler’s loupe. Real diamonds will have sharp edges and corners, while synthetic or fake diamonds may have rounded or blurred edges.
- Thermal conductivity test: This involves using a diamond tester to measure thermal conductivity. Real diamonds conduct heat better than any other gemstone, so if a diamond tester shows a high thermal conductivity reading, the gem is likely a real diamond.
- Fog test: Hold the diamond to your mouth, breathe on it, and quickly examine it. A real diamond will not retain moisture, so the fog will soon dissipate if it is real.
- UV light test: Diamonds will fluoresce under ultraviolet (UV) light. Place the diamond under a UV light and observe its fluorescence. Some diamonds may also show different fluorescence colors under long-wave and short-wave UV light.
- Refractivity test: Real diamonds refract light differently than other gemstones. Place the diamond on a newspaper or printed text and observe the text through the diamond. If you can see the text through the diamond, it is likely a fake.
- Certification: One of the most reliable ways to verify the authenticity of a colored diamond is to have it certified by a reputable gemological laboratory, such as the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) or the International Gemological Institute (IGI). These organizations have strict standards for grading and certifying diamonds, ensuring that the diamonds are real and accurately graded.
What Does A Colored Diamond Symbolize?
Colored diamonds, like other gemstones, have different meanings and symbolisms depending on their color. Here are some of the most common symbolic meanings associated with different colored diamonds:
- Yellow diamonds: Symbolize happiness, joy, and optimism. They are also associated with success, wisdom, and intellectual energy.
- Blue diamonds: Symbolize calmness, tranquility, and spiritual awareness. They are also associated with loyalty, trust, and integrity.
- Pink diamonds: Symbolize love, romance, and femininity. They are also associated with creativity, playfulness, and youthfulness.
- Red diamonds: Symbolize passion, energy, and power. They are also associated with courage, strength, and determination.
- Green diamonds: Symbolize nature, growth, and abundance. They are also associated with healing, balance, and harmony.
- Black diamonds: Symbolize mystery, sophistication, and strength. They are also associated with authority, power, and independence.
The meanings of colored diamonds are not fixed and may differ based on the person, culture, or situation. These meanings are symbolic in nature. Ultimately, the meaning of a colored diamond is subjective and can be whatever the wearer or admirer associates with it.

Uses of Colored Diamonds
Colored diamonds have been highly valued and used for various purposes throughout history. Here are some of the most common uses of colored diamonds:
- Jewelry: Colored diamonds are widely used in the jewelry industry, particularly in engagement rings, earrings, necklaces, and bracelets. They add a unique and striking touch to any piece of jewelry and can be used as the center stone or as accents.
- Investment: Colored diamonds are considered rare and valuable, making them a popular investment option for diversifying their portfolios. They can hold their value or appreciate over time, making them a long-term investment opportunity.
- Collection: Some people collect colored diamonds for their rarity and beauty. They may collect diamonds of a certain color or size or those with a particular history or story.
- Awards and honors: Colored diamonds are sometimes used as awards or honors to recognize achievements, such as in sports or entertainment industries.
- Scientific research: Colored diamonds are used in scientific research, particularly in physics, chemistry, and geology. They are used to study the Earth’s mantle, develop new technologies, and conduct experiments.
Which Gemstones Go Best With Colored Diamonds?
Colored diamonds can be paired with other gemstones to create stunning jewelry. Here are some gems that go well with colored diamonds:
- White Diamonds: Pairing colored diamonds with white diamonds creates a classic and timeless look. The white diamonds can be used as accents around the colored diamond to highlight its color or as the main stone in a two-stone ring.
- Sapphires: Blue sapphires complement blue diamonds beautifully, creating a monochromatic color scheme. Pink sapphires can also pair well with pink diamonds, creating a feminine and romantic look.
- Emeralds: Green emeralds pair well with green diamonds, creating a bold and vibrant look. They can also complement yellow diamonds, creating a warm and luxurious look.
- Rubies: Red rubies can be paired with red diamonds for a striking and dramatic look. They can also complement black diamonds, creating a sophisticated and elegant look.
- Tanzanite: Tanzanite is a relatively new gemstone that pairs well with purple diamonds, creating a modern and unique look.
Ultimately, the best gemstones to pair with colored diamonds depend on personal preference and the specific colors and styles of the jewelry piece.
Colored Diamonds As Birthstone
Colored diamonds belong to the diamond family and are used as birthstones. Although the traditional birthstone for April is a colorless diamond, colored diamonds have grown more popular as an alternative.
Each colored diamond is connected to a particular month and has its significance. For instance, pink diamonds are linked to April and symbolize love and romance, while blue diamonds symbolize March and strength and power.

How To Take Care Of Colored Diamonds Jewelry?
Colored diamond jewelry is a valuable and cherished possession. Here are some helpful tips on how to take care of colored diamond jewelry:
- Store the jewelry properly: When not wearing your colored diamond jewelry, store it in a soft pouch or jewelry box with separate compartments to prevent scratches and damage from other jewelry pieces.
- Clean the jewelry regularly: Use a soft-bristled brush, a mild solution of warm water, and gentle soap to clean your colored diamond jewelry. Avoid harsh chemicals, ultrasonic cleaners, or steamers that can damage the diamond and the metal.
- Handle the jewelry with care: When handling your colored diamond jewelry, avoid touching the diamond with your fingers, as the oils from your skin can dull its luster. Instead, hold the jewelry by the metal parts and avoid exposing it to chemicals, heat, or extreme temperatures.
- Take the jewelry for professional cleaning and maintenance: It is recommended to have your colored diamond jewelry inspected by a professional at least once a year. They can check for loose stones, worn prongs, and other issues that may affect the integrity and beauty of the piece.
- Insure the jewelry: Consider insuring your colored diamond jewelry to protect against loss, theft, or damage.
Following these tips can help keep your colored diamond jewelry looking its best and ensure its longevity and value.
FAQ
Are colored diamonds more expensive than white diamonds?
Colored diamonds are generally more expensive than white diamonds due to their rarity and unique color characteristics.
Can colored diamonds be treated or enhanced?
Some colored diamonds can be treated or enhanced to improve their color, clarity, or appearance. However, this can affect their value and authenticity, so buying from a reputable dealer and disclosing any treatments or enhancements is important.
How are Colored Diamonds Priced?
Colored diamonds are priced based on several factors, including their color intensity, carat weight, clarity, and cut. However, the most significant factor that affects the price of colored diamonds is the intensity and rarity of their color.
The pricing is based on a combination of subjective and objective factors. The objective factors include the carat weight, clarity, and cut, which are evaluated based on industry standards. The subjective factor is the color intensity and hue, which are assessed based on the opinion of a trained gemologist.
Which is the rarest colored diamond?
The rarest colored diamond is the red diamond, with only a handful of known specimens worldwide. Other rare colored diamonds include blue, green, and pink diamonds.







